How Java provides access protection using Packages
In this article, I will cover,
- What are Java Packages
- Types of Java Packages
- How to create a user-defined Package in Java
- How to Import Java Packages
- Sample Program to demonstrate access protection in Java using Packages
Video Tutorial – How Java provides access protection using Packages:
If a public or private access specifier is not used, then by default the classes, methods, data fields are accessible by any class in the same package.
This is called package-private or package-access.
TestClass.java is a class in package Test
//Java Program[TestClass.java]
package Test;
public class TestClass
{
public int a;
int b;
private int c;
public void fun1()
{
}
void fun2()
{
}
private void fun3()
{
}
} The main class named TestsMainClass.java imports the package Test
//Java Program[TestsMainClass.java]
import Test.TestClass;
public class TestsMainClass
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
TestClass obj = new TestClass();
obj.a = (int) 10; //allowed
obj.b = (int) 20; // error: cannot access
obj.c = (int) 30; //error: cannot access
obj.fun1(); //allowed
obj.fun2(); // error cannot access
obj.fun3(); //error cannot access
}
} In the above example,
We have created a package namely – Test. Inside the package Test there a class defined – TestClass
There are three data fields – a, b and c. The data field a is declared as public, b is defined as the default, and c is defined as private.
Simmilarly, fun1(), fun2() and fun3() are defined in the TestClass. fun1() is defined in public, fun2() in default and fun3() in private section.
TestsMainClass is the main class. Within this class, we are trying to access the data fields a, b and c.
Also, fun1(), fun2() and fun3() are accessed using the object of TestClass.
Data field a and fun1() are accessible in the main class. The remaining cannot be accessed as they are defined in the default and private section of TestClass of Test package.
The effect of access specifiers for class, subclass, or package is enlisted below,
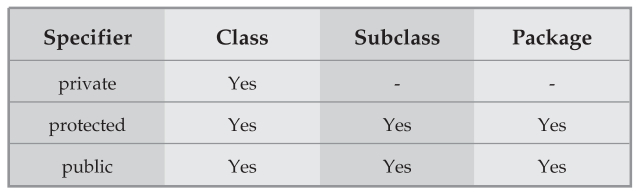
For example, if some variable is declared as protected, then the class itself can access it, its subclass can access it and any class in the same package can also access it. Similarly, if the variable is declared as private then that variable is accessible by that class only and its subclass can not access it.
If you like the tutorial share it with your friends. Like the Facebook page for regular updates and YouTube channel for video tutorials.
