Implementation of Simple Linear Regression in Python – Machine Learning
In this tutorial, we will understand the Implementation of Simple Linear Regression in Python – Machine Learning.
Importing the Necessary libraries
To begin the implementation first we will import the necessary libraries like NumPy for numerical computation, MatPlotlib for visualization, and pandas for reading the dataset.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd
Importing the dataset
Next, we import or read the dataset. Click here to download the salary dataset used in this implementation. The dataset has two features YearsExperience and Salary. After reading the dataset, divide the dataset into concepts and targets. Store the concepts into X and targets into y.
dataset = pd.read_csv('Salary_Data.csv')
X = dataset.iloc[:, :-1].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, -1].valuesNext, display the first five rows of the salary dataset using head() function from pandas.
dataset.head()
| YearsExperience | Salary | |
| 0 | 1.1 | 39343.0 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.3 | 46205.0 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 37731.0 |
| 3 | 2.0 | 43525.0 |
| 4 | 2.2 | 39891.0 |
Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
Next, divide the dataset into two parts, training and testing using the train_test_split function from sklearn. The test_size and random_state attributes are set to 1/3 and 0 respectively. You can change these attributes as per your requirements.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 1/3, random_state = 0)
Training the Simple Linear Regression model on the Training set
A Linear Regression algorithm is used to create a model. The LinearRegression function is imported from sklearn.linear_model library.
ffrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression regressor = LinearRegression() regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
Simple Linear Regression classifier model
LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None, normalize=False)
Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
pd.DataFrame(data={'Actuals': y_test, 'Predictions': y_pred})| Actuals | Predictions | |
| 0 | 37731.0 | 40835.105909 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 122391.0 | 123079.399408 |
| 2 | 57081.0 | 65134.556261 |
| 3 | 63218.0 | 63265.367772 |
| 4 | 116969.0 | 115602.645454 |
| 5 | 109431.0 | 108125.891499 |
| 6 | 112635.0 | 116537.239698 |
| 7 | 55794.0 | 64199.962017 |
| 8 | 83088.0 | 76349.687193 |
| 9 | 101302.0 | 100649.137545 |
Visualising the Training set results
Here scatter plot is used to visualize the results. The title of the plot is set to Salary vs Experience (Training set), xlabel is set to Years of Experience, and ylabel is set to Salary.
plt.scatter(X_train, y_train, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_train, regressor.predict(X_train), color = 'blue')
plt.title('Salary vs Experience (Training set)')
plt.xlabel('Years of Experience')
plt.ylabel('Salary')
plt.show()Visualising the Test set results
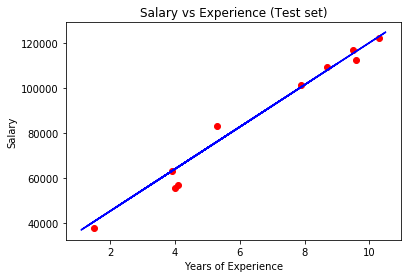
The title of the plot is set to Salary vs Experience (Test set), xlabel is set to Years of Experience, and ylabel is set to Salary.
plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_train, regressor.predict(X_train), color = 'blue')
plt.title('Salary vs Experience (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('Years of Experience')
plt.ylabel('Salary')
plt.show()Summary:
In this tutorial, we understood, the Implementation of Simple Linear Regression in Python. If you like the tutorial share it with your friends. Like the Facebook page for regular updates and YouTube channel for video tutorials.